Rostral Oral Cavity
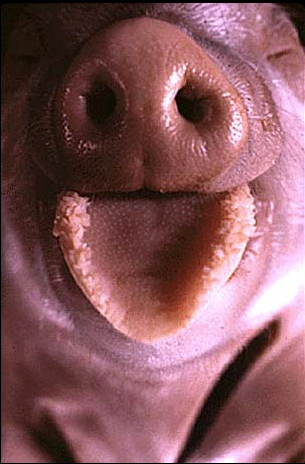
The tongue often protrudes from the anterior opening of the oral cavity. The tongue is a highly manipulative, muscular structure, that contributes to chewing, swallowing, and sensing food.
Chemical sensation occurs at sensory papillae, visible on the tongue. Taste cells within buds of the papillae detect chemical features that the brain interprets as salty, sweet, sour, and bitter (in humans).
The detection of chemicals by structures in the snout/nose is important, and also associated with taste. The two nares (commonly called nostrils) allow air into the nasal cavity for olfactory sensation, warming, and respiration.
Next: Inside the oral cavity
Back to: Digestive system
Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection